3.3.2 Quantum circuit for bell states
A Bell state, also known as an entangled state or EPR pair(Einsten-Podolsky-Rosen pair), is a specific type of entangled quantum states involving two qubits that are entangled. They exhibit the phenomenon of entanglement, where the state of one qubit is dependent on the state of the other, no matter how far they are.
Bell states and Bell inequalities
The concept of Bell states is closely associated with Bell inequalities, which were introduced by physicist John Bell in 1964. Bell inequalities provide a way to test whether the correlations observed between entangled particles can be explained by classical physics or if they require a quantum explanation. Violations of Bell inequalities indicate that the system can not be described by local hidden variable theory and confirm the presence of quantum entanglement.
The four bell states
There are four bell states, which are denoted as \(|\Phi^+>, |\Phi^->, |\Psi^+> \text{and} |\Psi^->\). These states are given by:
\[ |\Phi^+\rangle = \frac{1}{\sqrt{2}} \left( |00\rangle + |11\rangle \right) \] \[ |\Phi^-\rangle = \frac{1}{\sqrt{2}} \left( |00\rangle - |11\rangle \right) \] \[ |\Psi^+\rangle = \frac{1}{\sqrt{2}} \left( |01\rangle + |10\rangle \right) \] \[ |\Psi^-\rangle = \frac{1}{\sqrt{2}} \left( |01\rangle - |10\rangle \right) \]Construct Bell States using quantum circuits
Bell states can be constructed using a H gate and a CNOT gate:
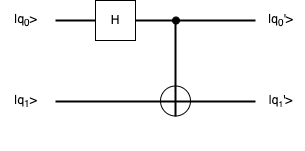
1. Initial the input qubit |q0> = |0> and |q1> = |0>,
2. Apply a H gate to the first qubit: creates a superposition,
\[ |0>|0> \xrightarrow{H_{0}} H|0>|0> = \frac{1}{\sqrt{2}}(|0>+|1>)|0> \]3. Apply a CNOT gate, with the first qubit as the control and the second qubit as the target: This entangles the two qubits,
\[ \frac{1}{\sqrt{2}}(|0>+|1>)|0> \xrightarrow{CNOT_{01}} \frac{1}{\sqrt{2}}(|00> + |11>) \]We can get The bell state \(|\Phi^+>\):
\[ |\Phi^+> = \frac{1}{\sqrt{2}}(|00> + |11>) \]