3.3.5 Quantum binary multiplication
The method is from the paper[2] that introduce the detailed process of constructing quantum multiplication. In classical multiplication, each digital of one number A is multiplied by each digital of another number B, and then add up the results according to their place values.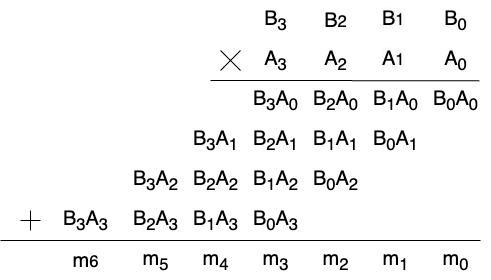
The method of quantum multiplication is to construct two binary number multiplication and full adder. The binary numbers A and B are represented using qubits. Toffoli gate is used to perform multiplication computation between qubits. After multiplication, the results are added together using a quantum full adder. For example, firstly, the binary numbers A(\(A_3A_2A_1A_0\)) and B(\(B_3B_2B_1B_0\)) are encoded by qubits. In the second step, \(B_3A_0\), \(B_2A_0\), \(B_1A_0\), and \(B_0A_0\) are constructed respectively, then the results are added together. The second step is continued to perform repeatedly until all the binary number of A and B are computed.
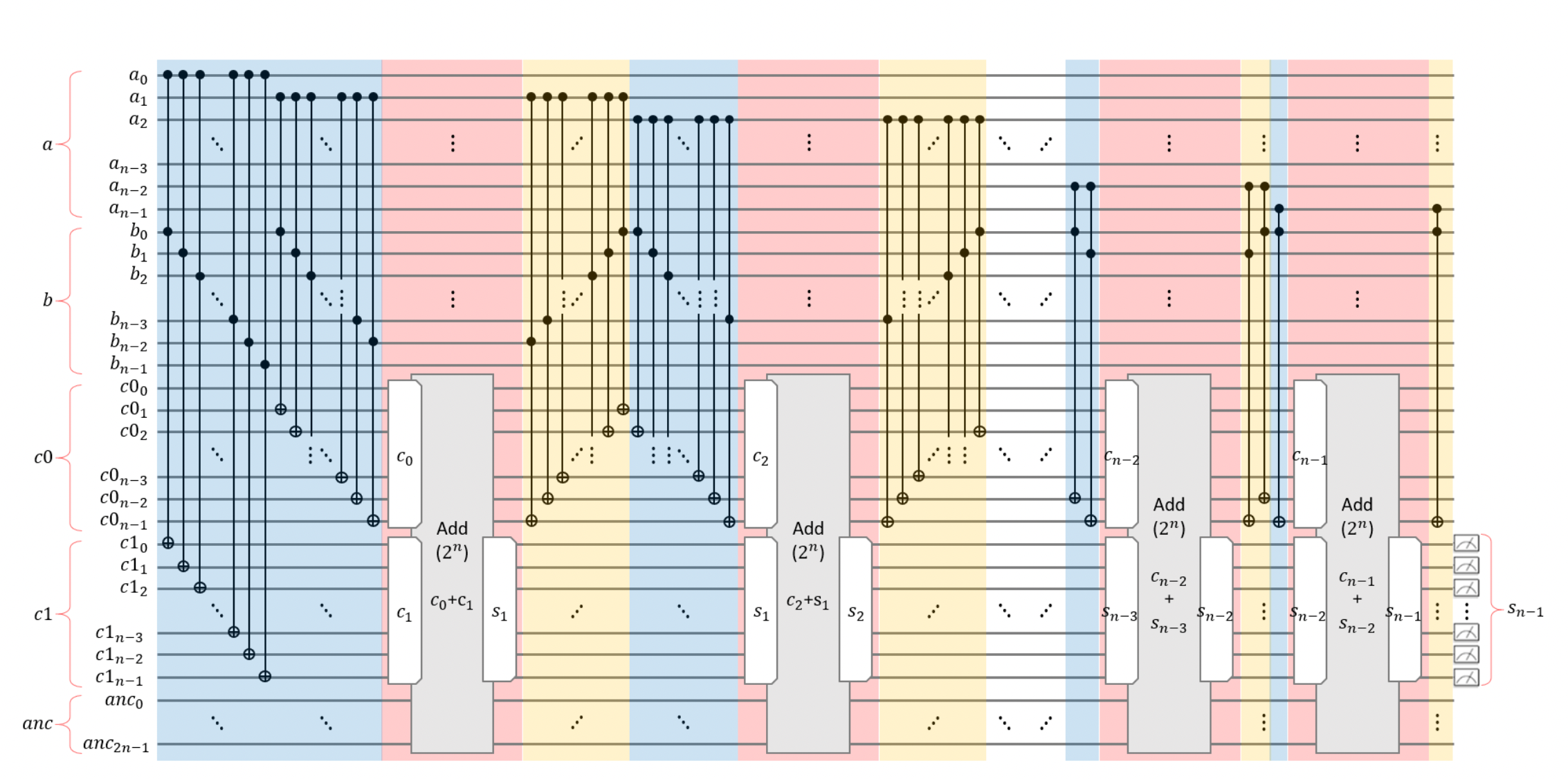
In the blue part of the figure, Ai and B0 ... Bn-1 are multiplied respectively using Toffoli gates. In the red part of the figure, a full adder is used to add the outputs of C0 and C1. In the yellow part, the C0 is recovered to the quantum states |000>. This is because it needs to continue to perform Ai and B0 ... Bn-1 multiplication.
For example, I built a quantum circuit to multiple two numbers mod \(2^3\) with the binary length of 3. The first three qubits (q0, q1, q2) encode A, qubits (q3, q4, q5) encodes 8, qubits (q6, q7, q8) represents \(A_i * B_j\), qubits (q9, q10, q11) represents A0 * B0, A0 * B1, A0 * B2, qubits (12, 13, 14) represents the sum of the first addition(A0*B2 A0*B1 A0*B0 + A1*B1 A1*B0), qubit q15 represents the carry, qubits (16, 17, 18) represents the sum of the second addition (qubits(12, 13, 14) + A2*B0), qubit 19 represents the carry. The final result is qubits (16, 17, 18), the carry deleted because it needs to mod 8.
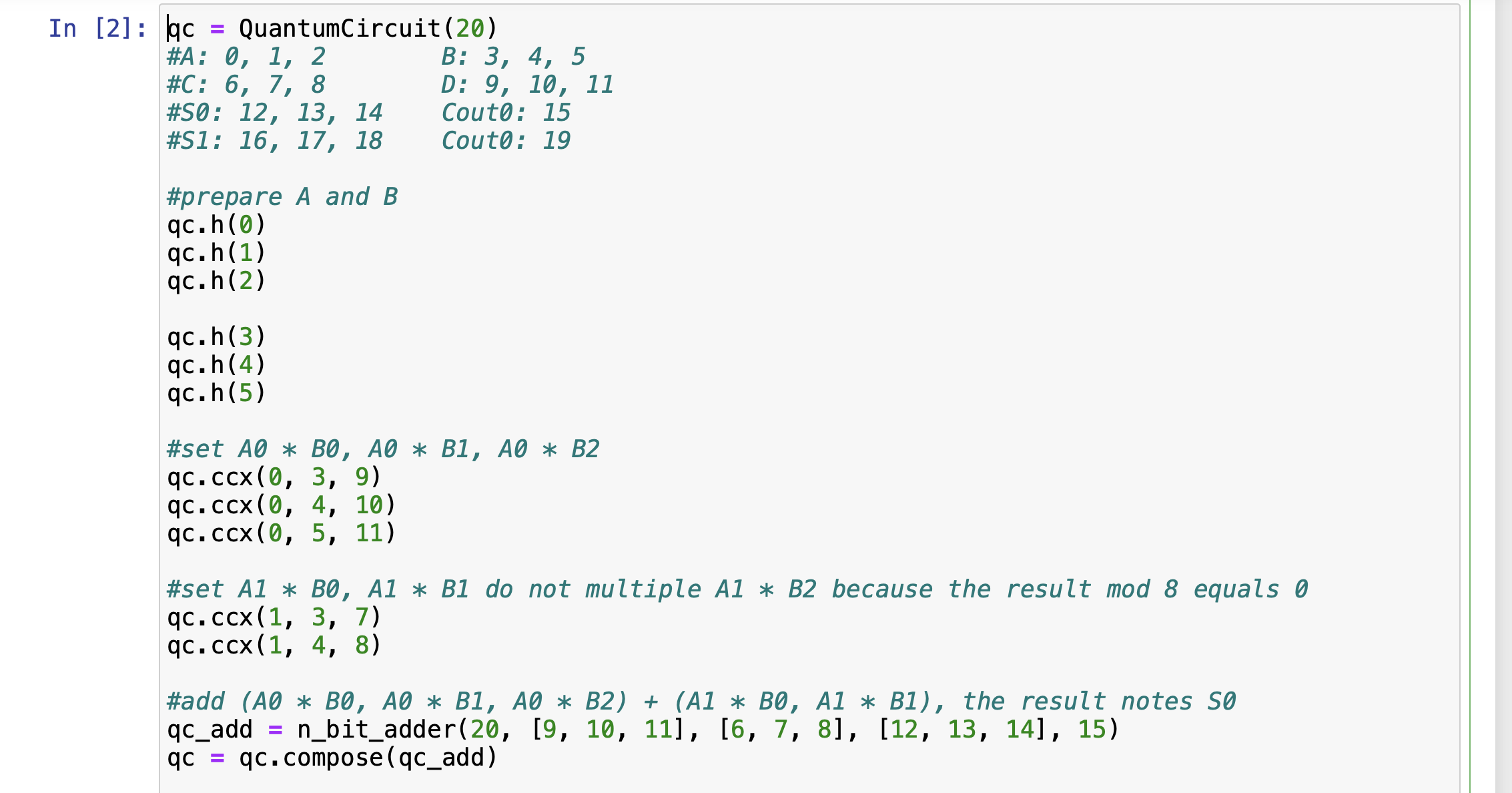
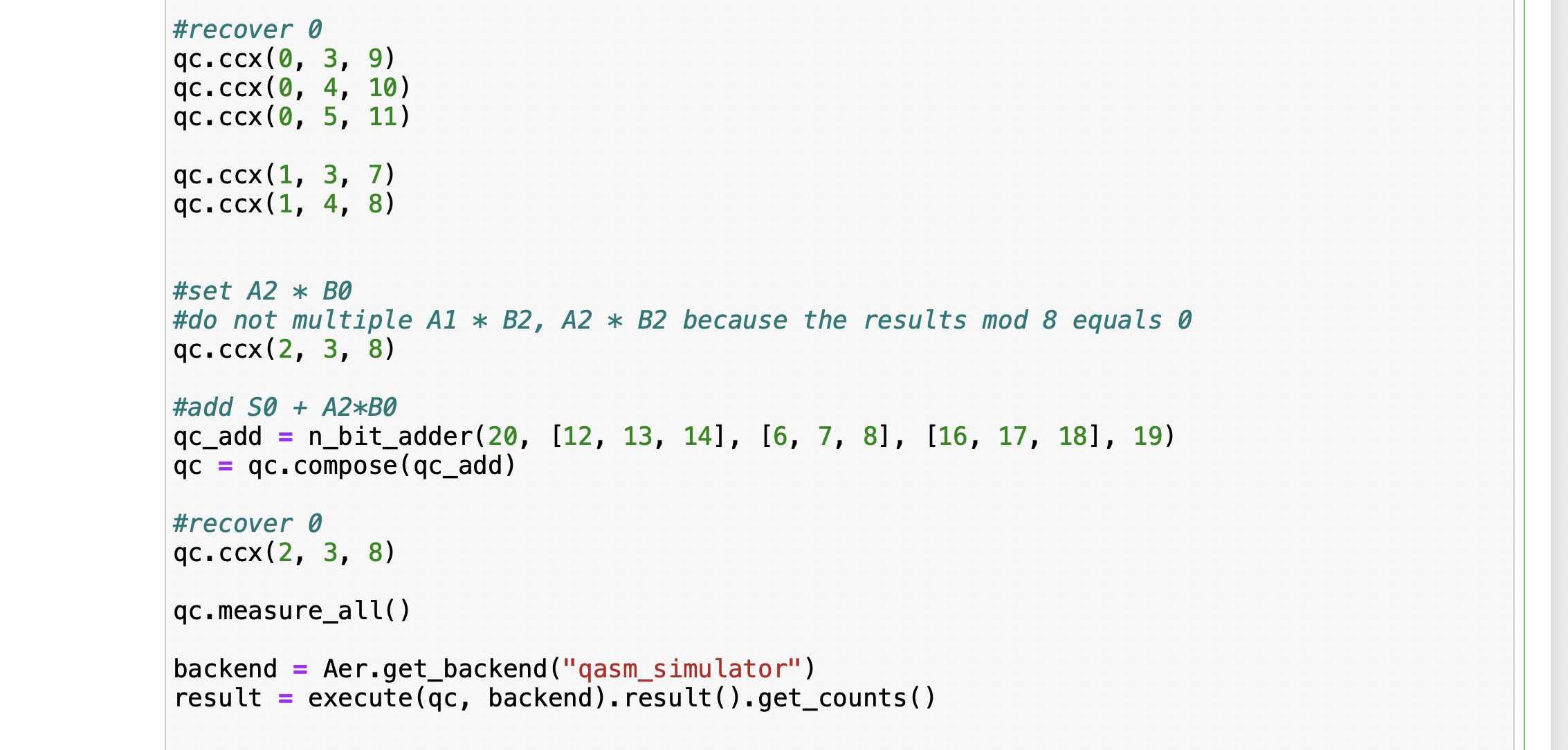
Qiskit example lists A and B range from 0 and 15 and the final results mod 8. It requires the number of qubits
\(L_a\) represents the length of the encoding binary string of A or B. \(L_c\) represents the length of the encoding binary string of the final result. In the example, \(L_a\) and \(Lc\) are 3 so the length of qubits is 20.